Application
Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular Vesicles serve as critical mediators of intercellular communication and exhibit diverse biological functions with substantial implications for both normal physiological processes and disease states. The isolation of exosomes represents a pivotal step in exosome research; however, it is associated with several challenges, particularly concerning purity, yield, integrity, and cost-effectiveness. EXODUS is capable of rapidly removing free nucleic acids and protein impurities from samples, thereby achieving efficient purification and enrichment of exosomes. Through the use of a nanoporous membrane, exosomes are precisely intercepted, enabling a highly targeted and selective isolation process. Consequently, EXODUS holds great promise for transforming exosome isolation techniques and facilitating groundbreaking discoveries in biomedical research and clinical translation.
Cases
Case 1: Urine
Urine EV Isolation With EXODUS H-600
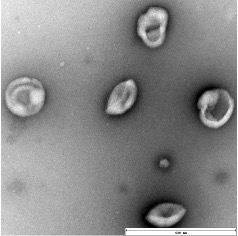
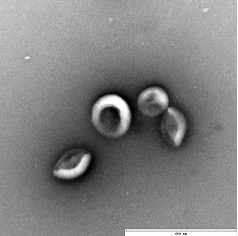
Characterization of exosome by transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
TEM of exosome harvested from urine by EXODUS, showing the characteristic cup and plate shape of exosome. Scale bar = 600 nm.
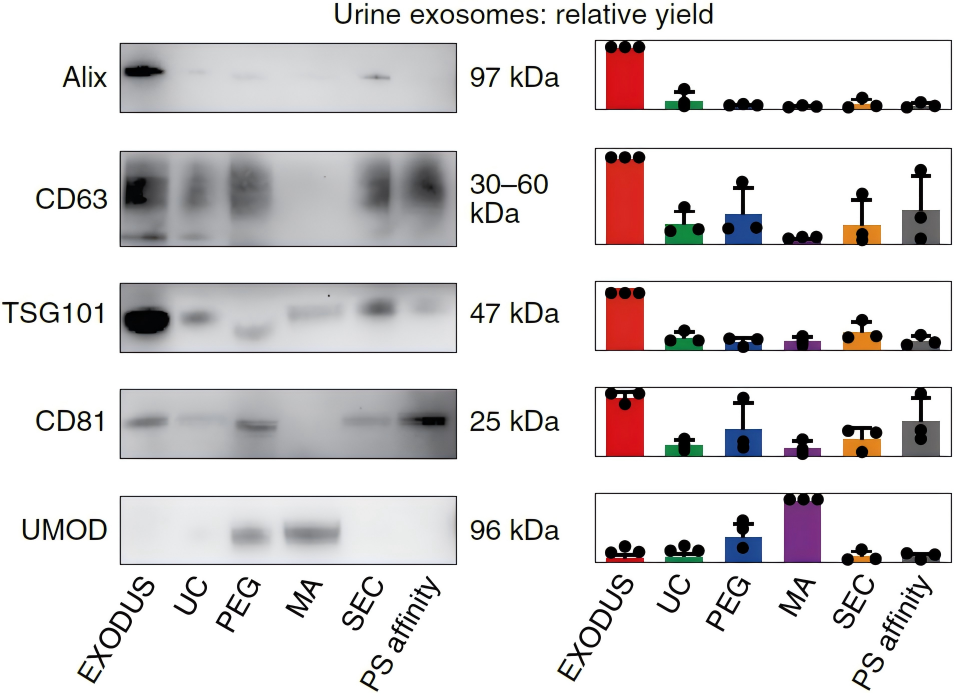
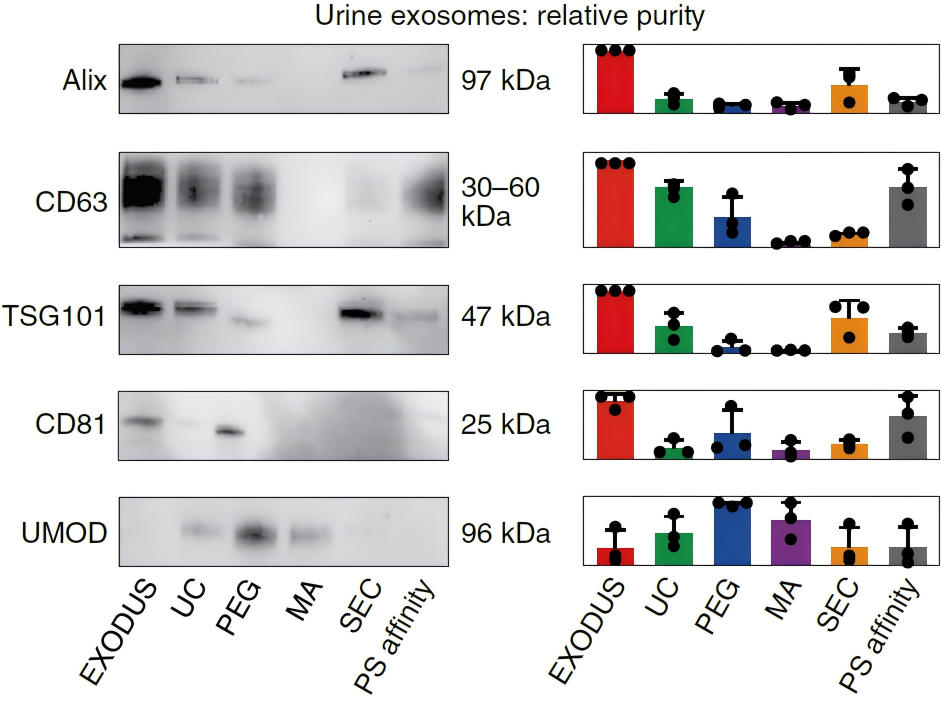
Method comparison for exosome isolation.
Western blot analysis of exosomal markers (Alix, CD63, TSG101, and CD81) and impurity Uromodulin (UMOD) of exosome isolated using methods of EXODUS H-600, Ultracentrifugation (UC), PEG precipitation, Membrane affinity (MA), Size exclusion chromatography (SEC), and Phosphatidylserine (PS) affinity, respectively. Compared to other methods, exosome isolated by EXODUS H-600 shows higher relative yield and purity in WB gel graph (left) and bar graph of normalized band intensity (right).
Case 2: Cell Culture Medium
(1) Cell Culture Medium EV Isolation With EXODUS H-600
Characterization of exosomes by TEM.
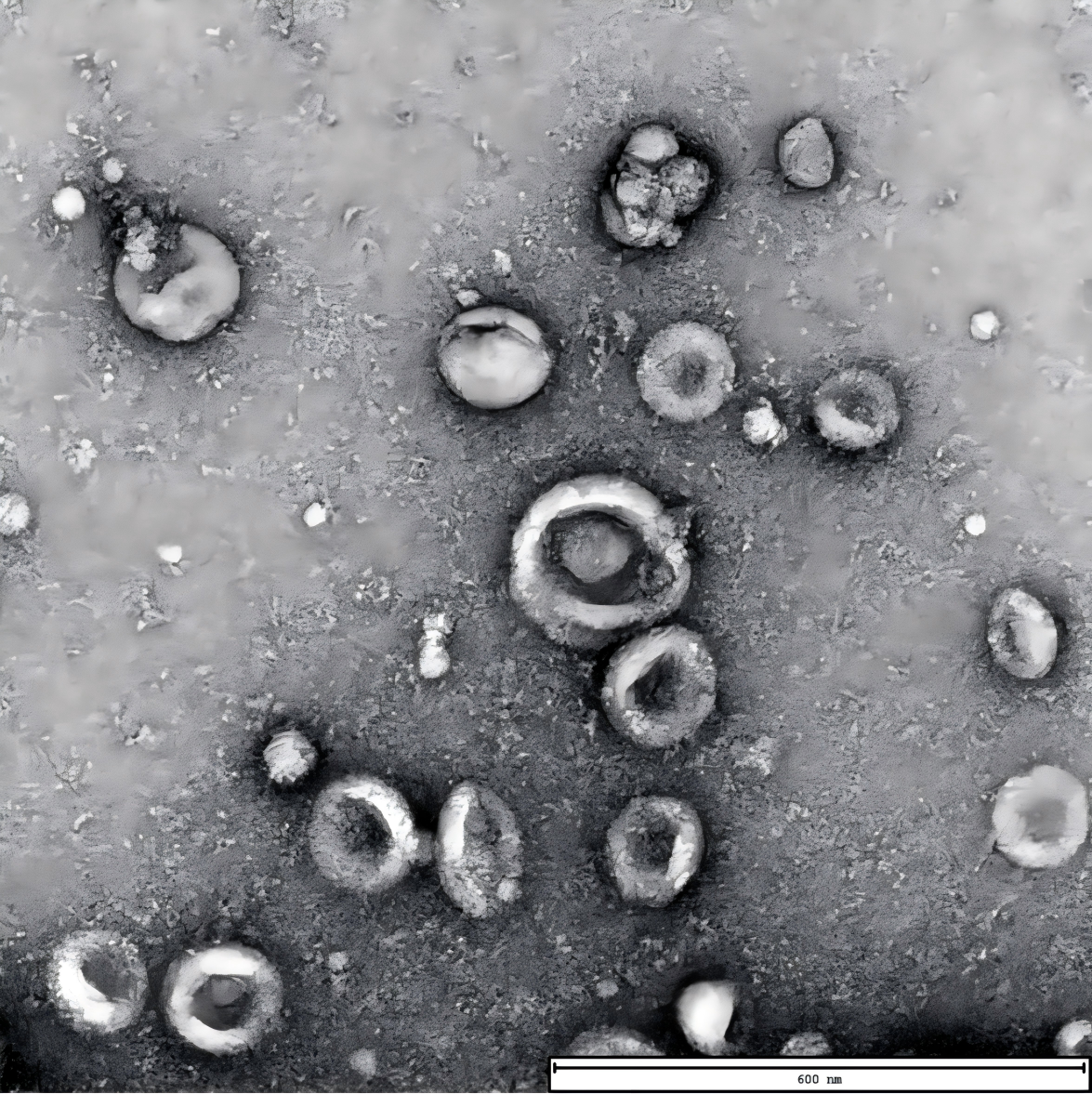
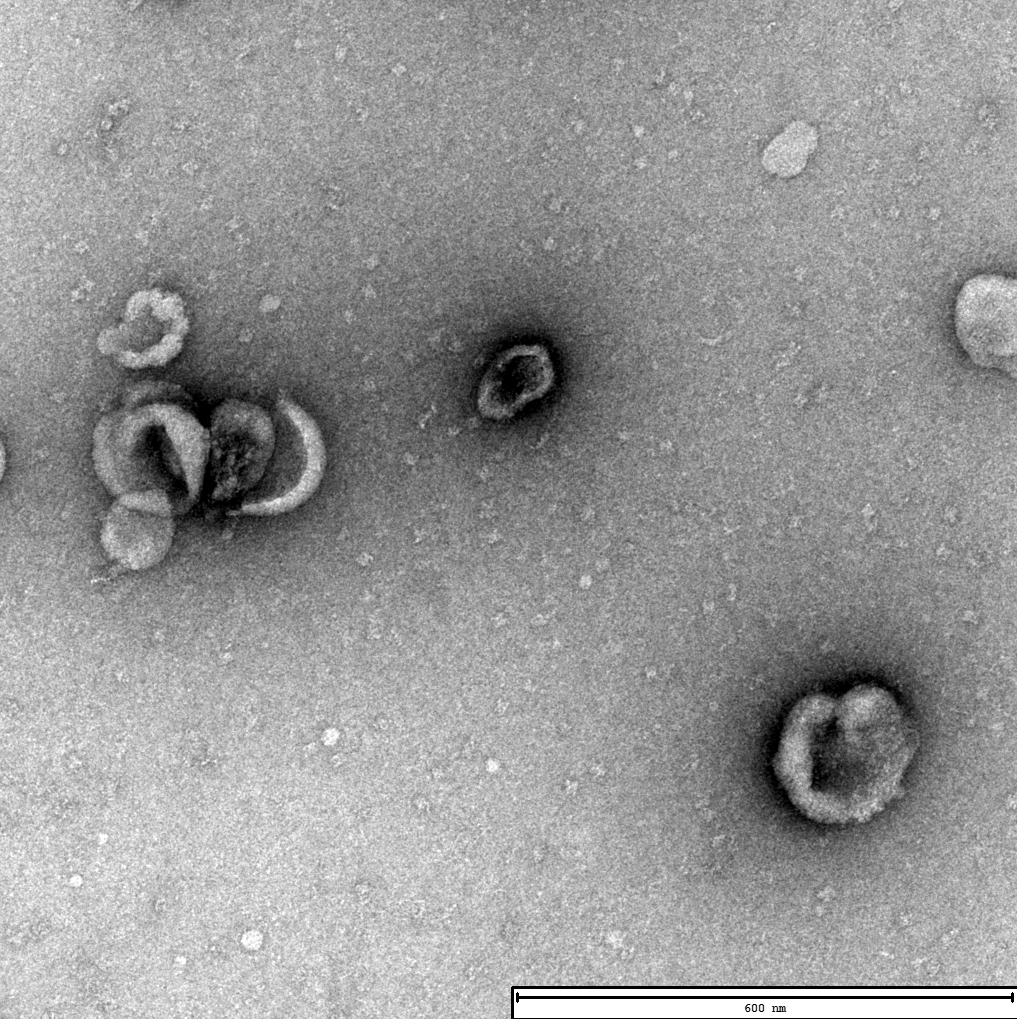
Electron micrographs of exosomes isolated from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell supernatants using EXODUS H-600 (left) and UC (Right). TEM of exosomes obtained from EXODUS shows such typical cupped structure, more exosomal vesicular particles, and less particle aggregation compared to that from UC. Scale bar=600 nm
Exodus
UC
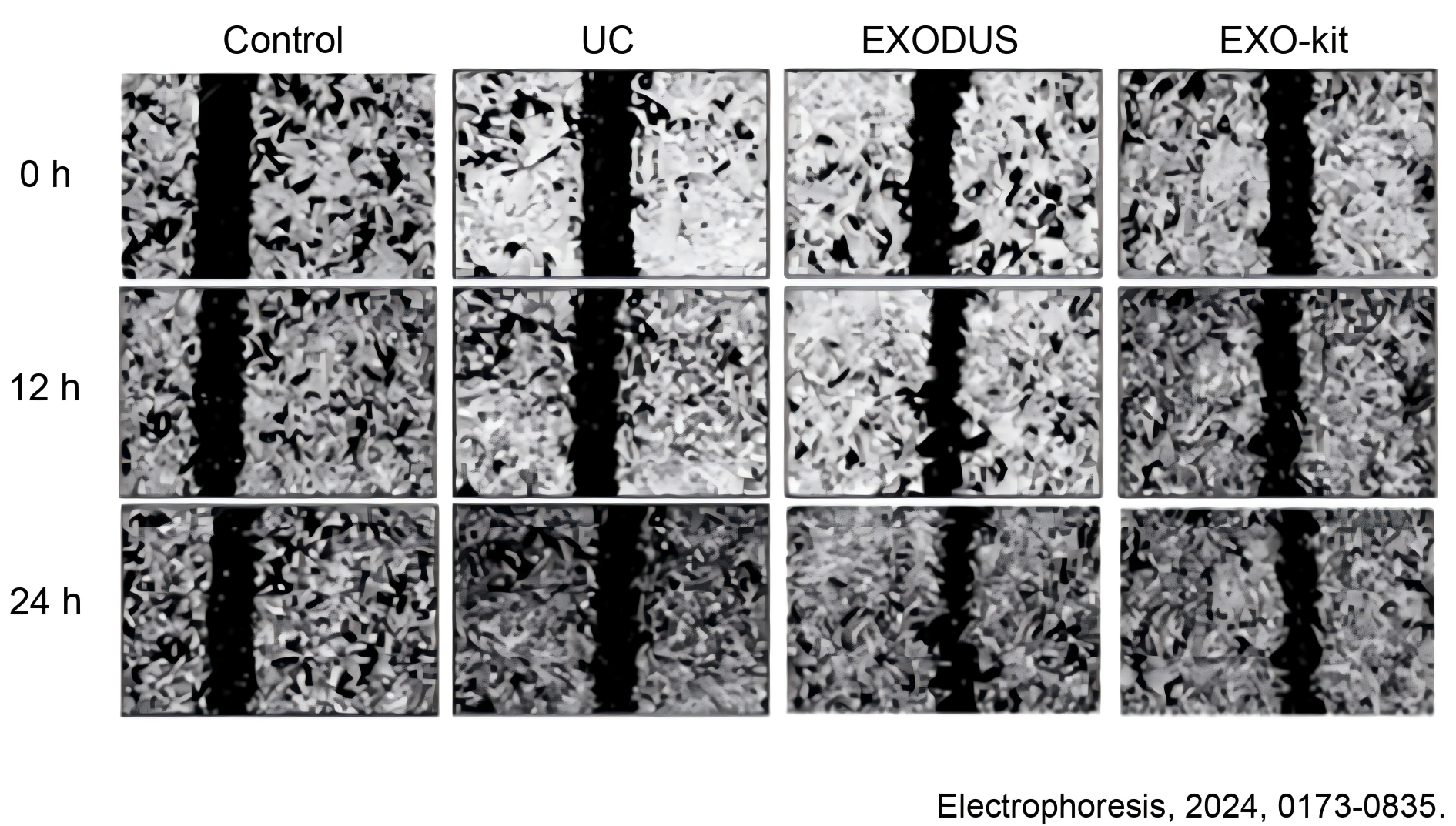
Scratched wound assay for the effects evaluation of exosomes on migration capacity of cells
Cells began to exhibit significantly migration 12h after treatment with exosomes isolated either from EXODUS H-600 or EXO-kit compared to that from UC and the control group. After 24h, enhanced cell migration was observed from the group with the addition of EXODUS H-600 isolated exosome. Scale bar = 40 μm.
(2) Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived EV Isolation With EXODUS T-2800
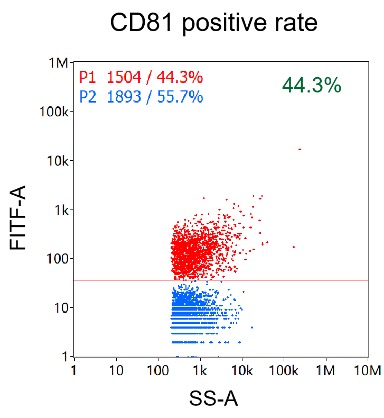
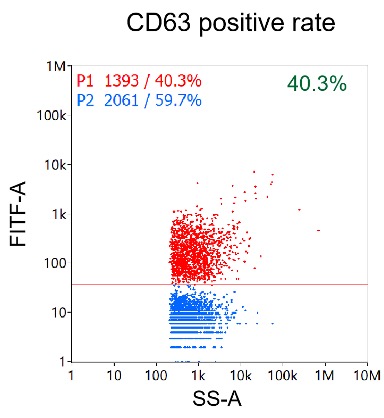
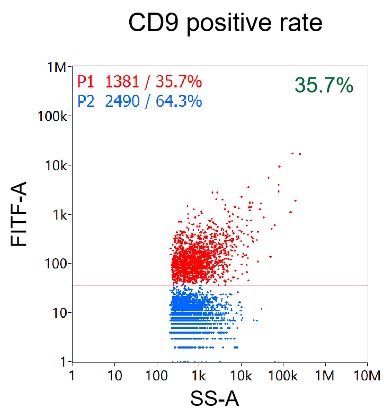
Nanoflow cytometry analysis of particles isolated from Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) by EXODUS T-2800.
Measured positive percentages of CD81, CD9, and CD63 on EVs were 43%, 40.3%, and 35.7%, respectively.
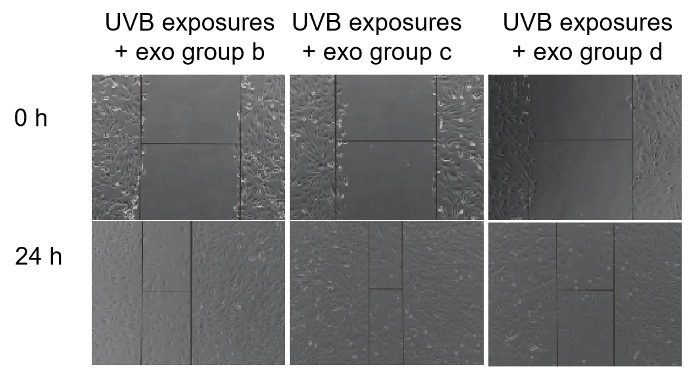
Effect of EXODUS T-2800 isolated exosomes on alleviating UVB-induced cellular stress.
Exosomes derived from MSCs of different generations (Groups a-d) were tested for their ability to mitigate UVB-induced cellular damage. Group c, derived from MSCs of a specific generation, demonstrated the most significant protective effect, highlighting the potential of exosome-based therapies in UVB-induced cellular injury.

(3) 293F Culture Medium EV Isolation With EXODUS T-2800
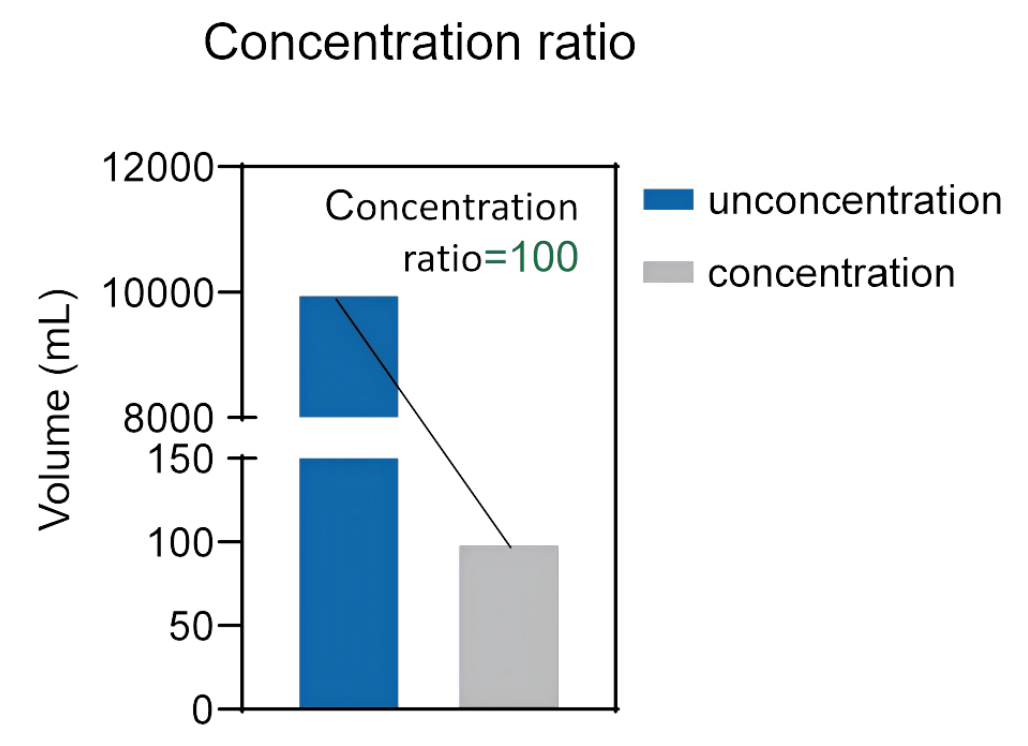
Large volume of culture medium process by EXODUS T-2800
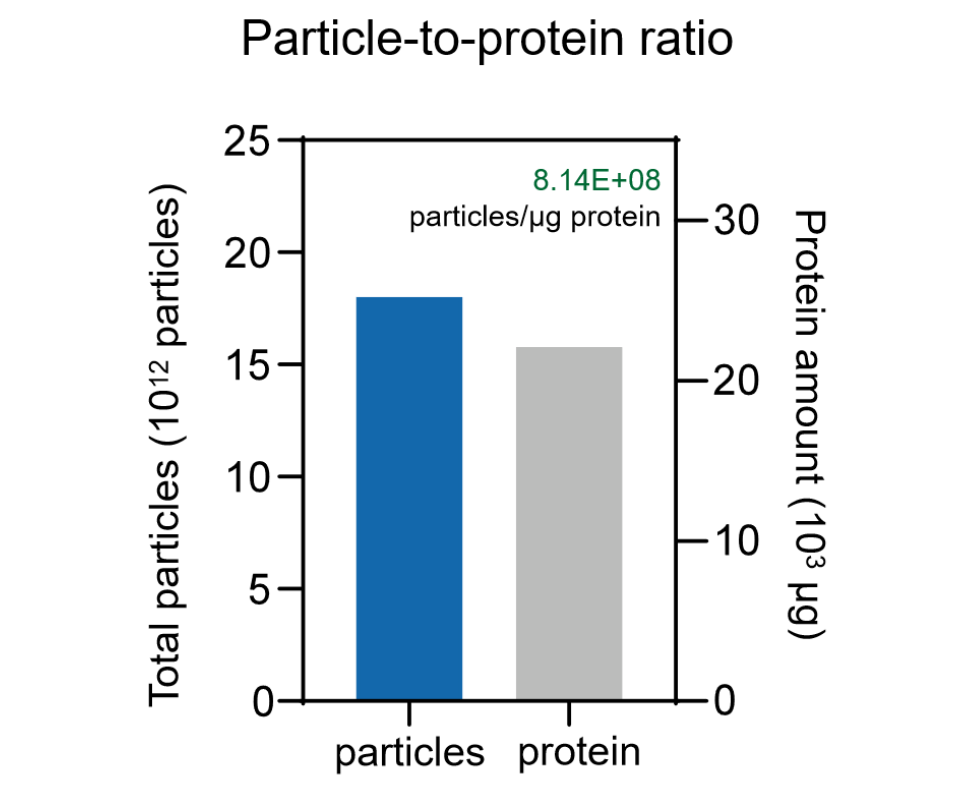
EXODUS T-2800 was capable of concentrating the 10 L 293F Culture medium to the final volume of 100 ml (Left) and recovering pure EVs with particle-to-protein ratio of 8.14x 108 particles/μg protein(right).
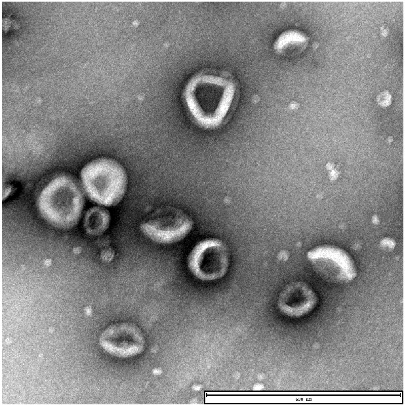
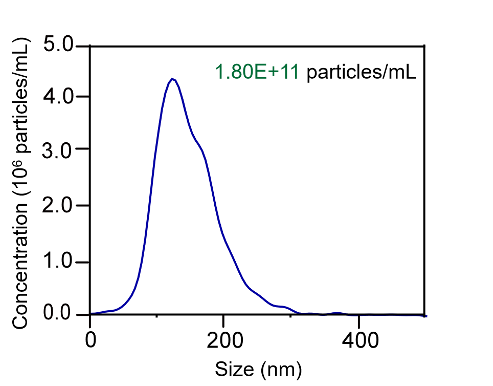
Characterization of EVs harvested from 293F culture medium by EXODUS.
(Left) Transmission electron microscopy showed the characteristic cup and plate shape of exosome. Scale bar = 600 nm. (Middle) Western blot analysis revealed the expression of exosome-positive markers CD9, CD81, TSG101, and HSP90, while the negative markers Calnexin and GM130 were undetectable. (Right) The NTA data shows that the size distribution of EVs particle with the median size of 100 nm and the concentration of1.8×1011 particles/mL.
TEM
WB Analysis

Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
Case 3: Plasma
(1) Plasma EV Isolation With EXODUS H-600
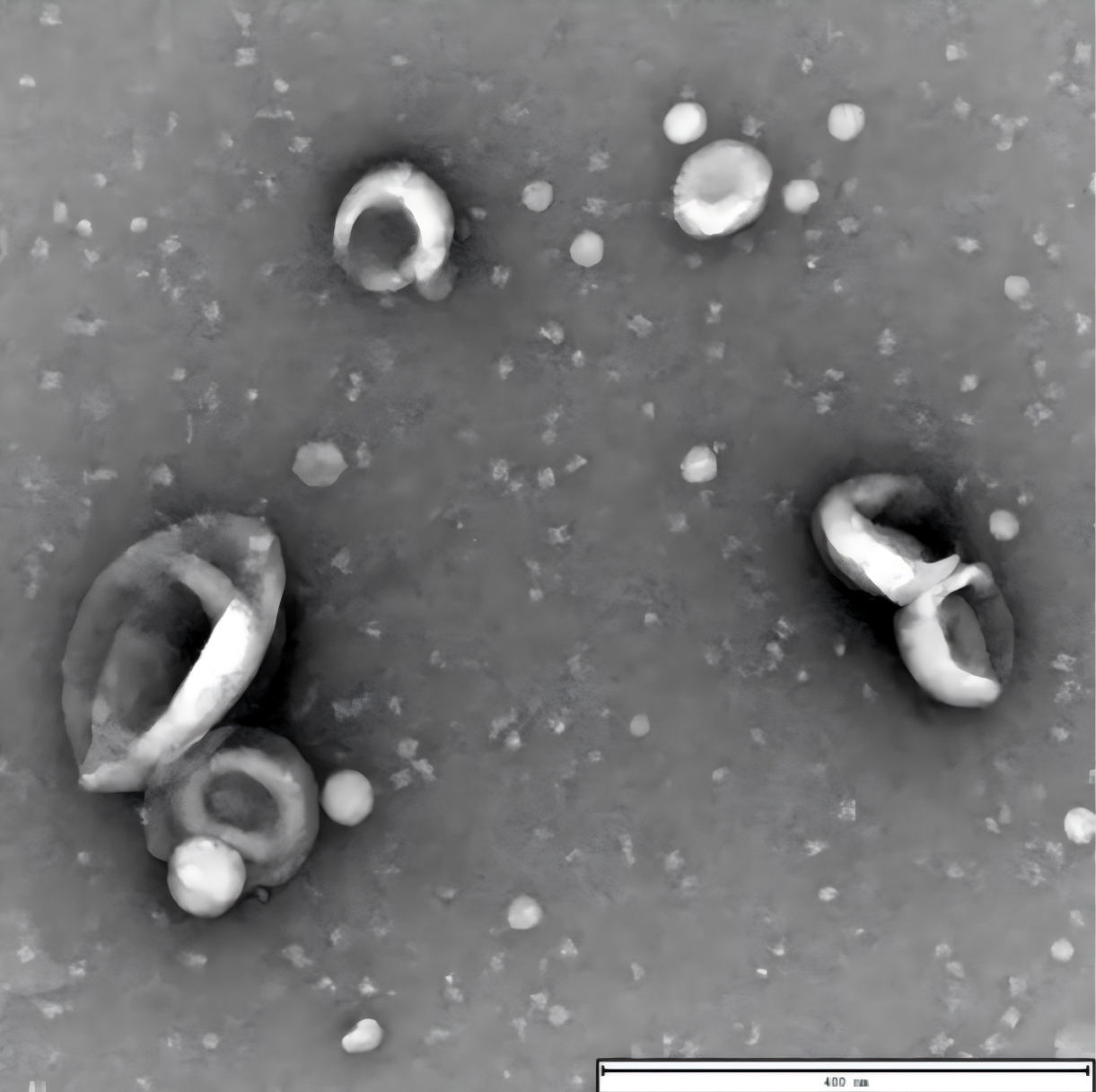
Characterization of exosomes by TEM.
TEM analysis of exosomes isolated from the plasma of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using the EXODUS reveals their distinctive cup-shaped and plate-like morphology. Scale bar = 400 nm
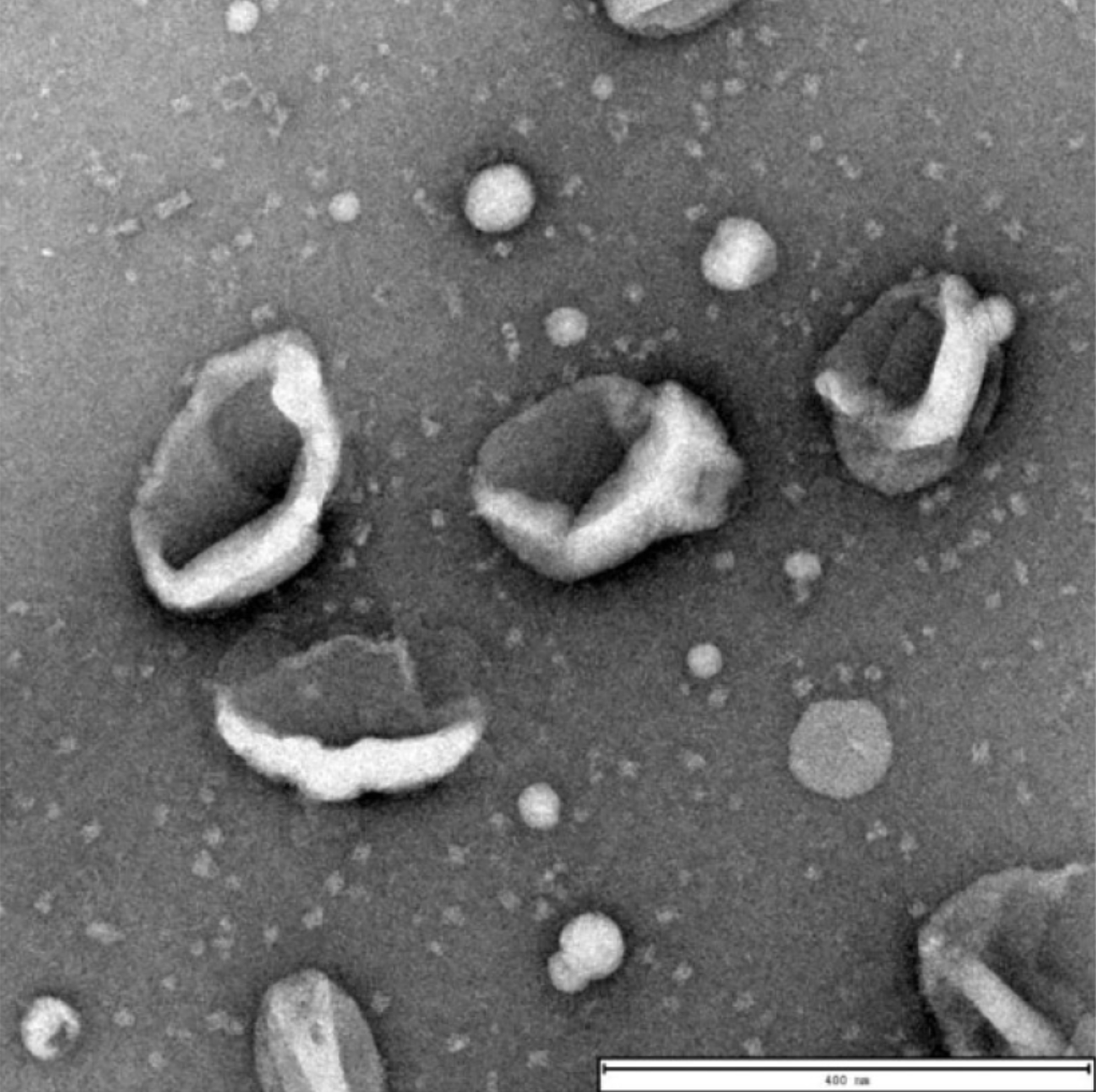
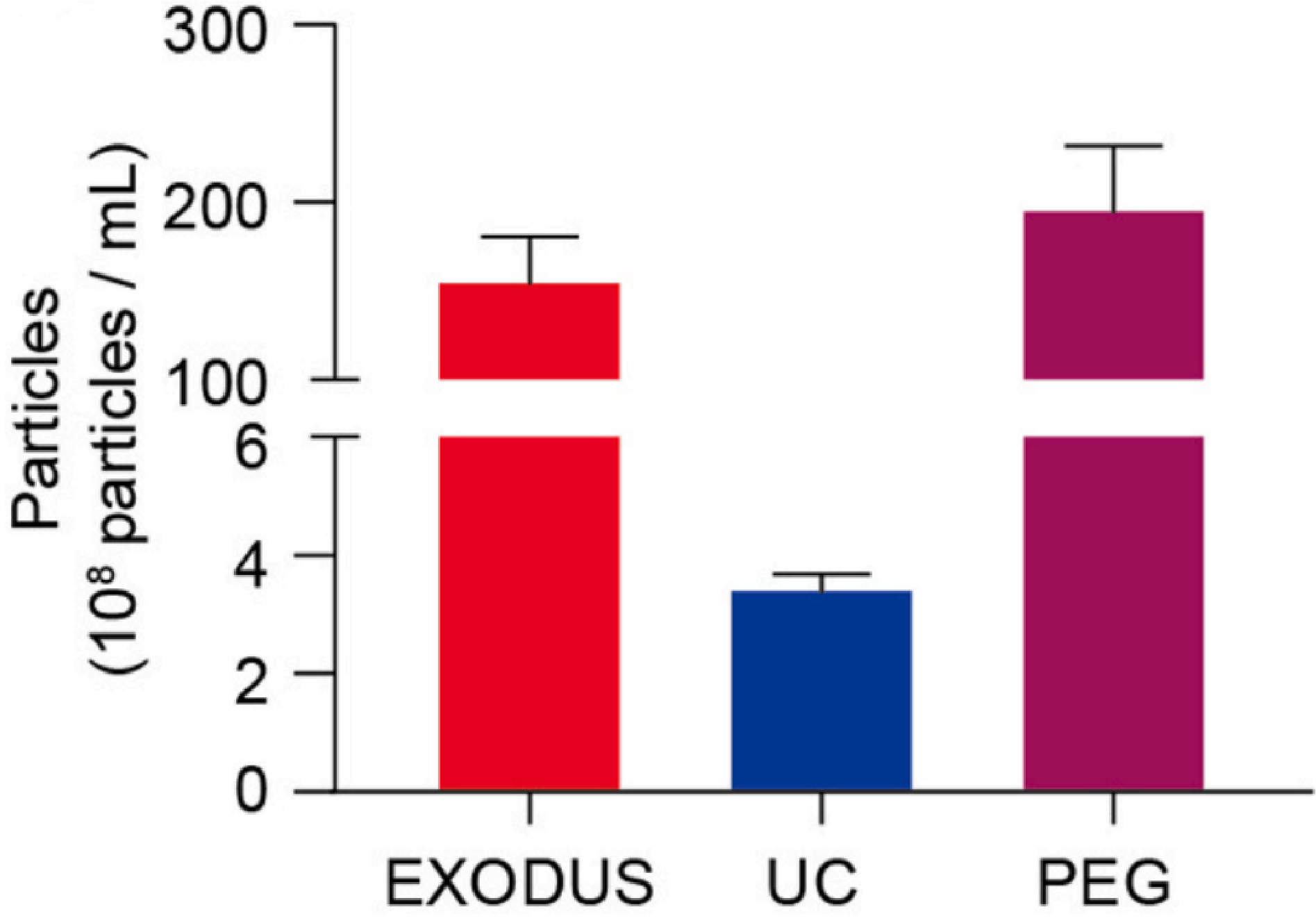
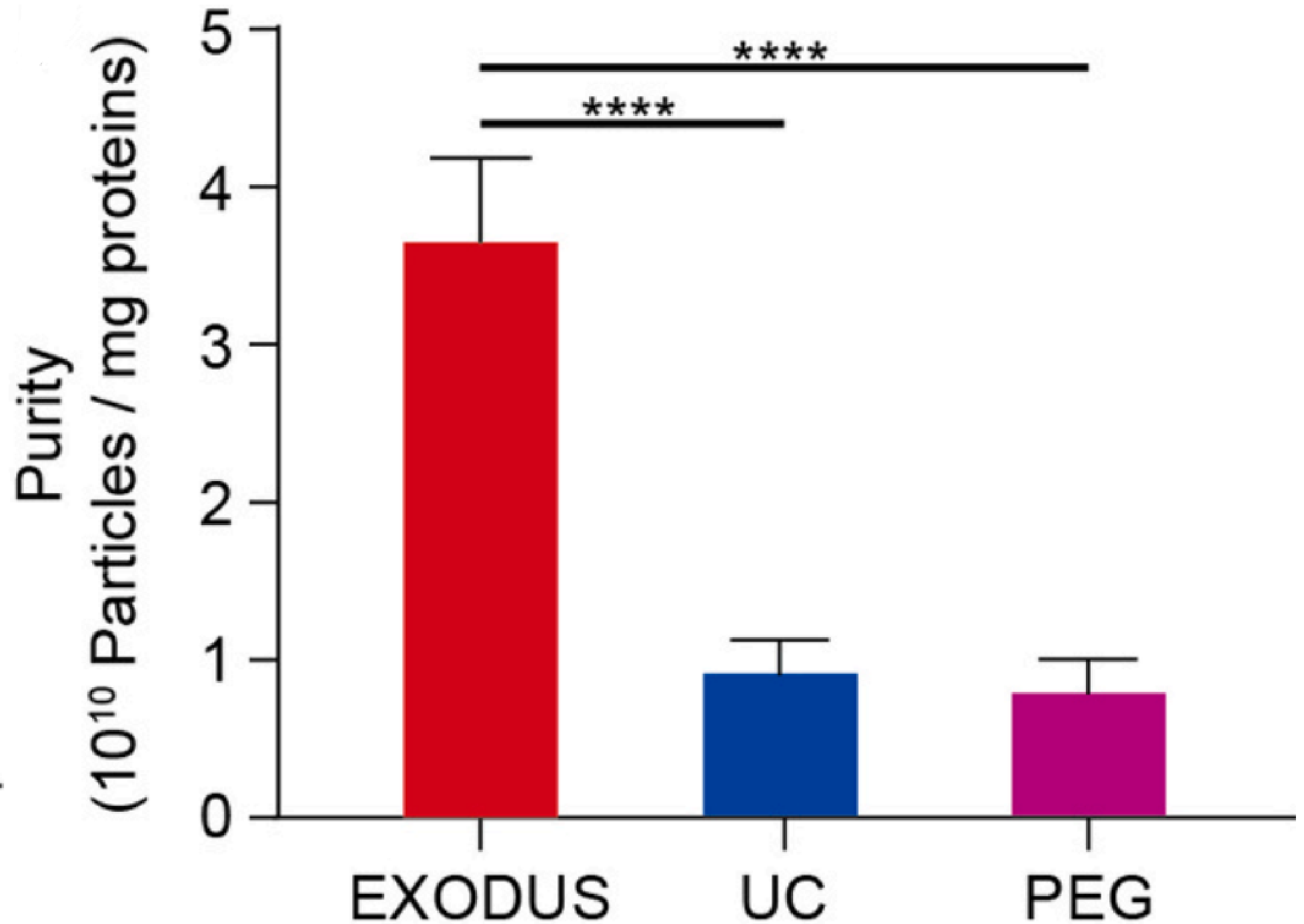
The yield and purity analysis of sEVs isolated by methods of EXODUS H-600, UC, and PEG, respectively.
sEVs isolated using EXODUS or PEG from 20 μL of plasma (approximately 2 x 1010 particles/mL) showed over a 50-fold increase compared to those isolated using UC. The purity of sEVs isolated using EXODUS was more than three times higher than that achieved with UC or PEG.
(2) Plasma EV Isolation With EXODUS T-2800
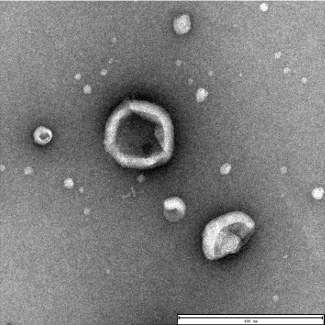
Characterization of plasma EVs isolated by EXODUS T-2800.
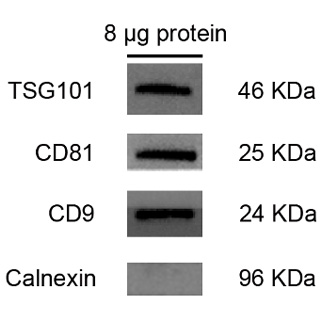
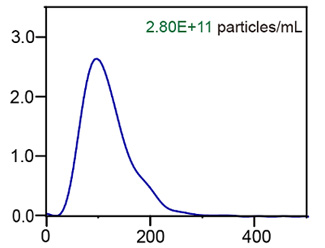
(Left) TEM revealed the characteristic cup- and plate-like shapes of exosomes. Scale bar = 400 nm. (Middle) Western blot analysis confirmed the presence of exosome markers TSG101, CD81, and CD9, while the negative marker Calnexin was undetectable. (Right) NTA showed a median particle size of 100 nm and a concentration of 2.8 × 1011 particles/mL.
TEM
WB Analysis
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
Case 4: Trace Sample
(1) Trace Sample EV Isolation With EXODUS H-600
Characterization of tears EVs and aqueous humor EVs by TEM.
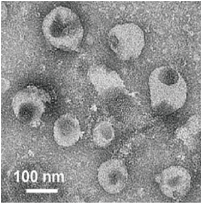
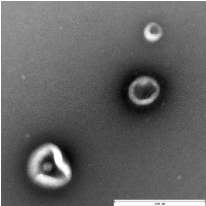
TEM images of exosomes derived from two trace samples of 50 μL tear fluid (left, scale bar = 100 nm) and 150 μL aqueous humor (right, scale bar = 400 nm) using the EXODUS, reveals their characteristic cup-shaped and plate-like morphological features.
Tear EV
Aqueous Humor EV
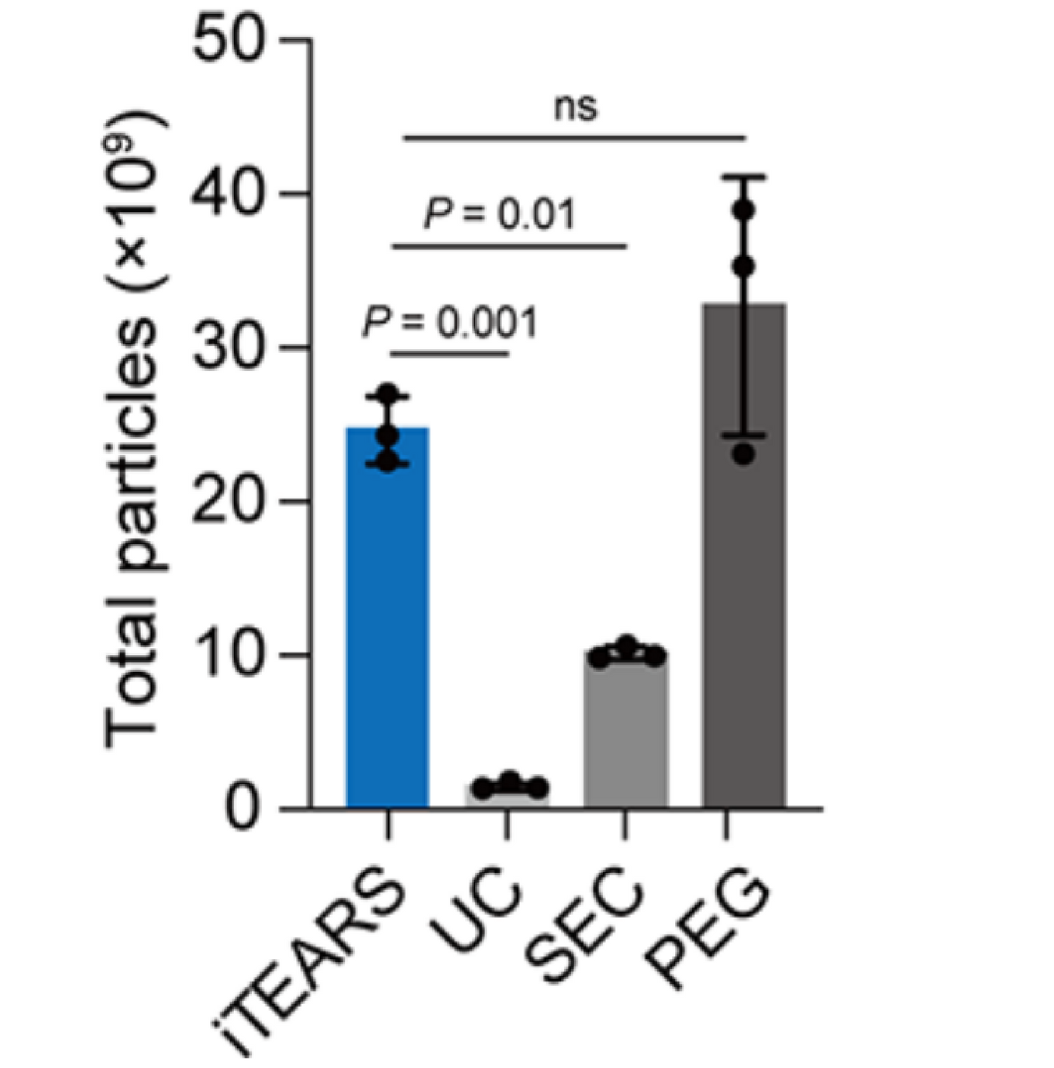
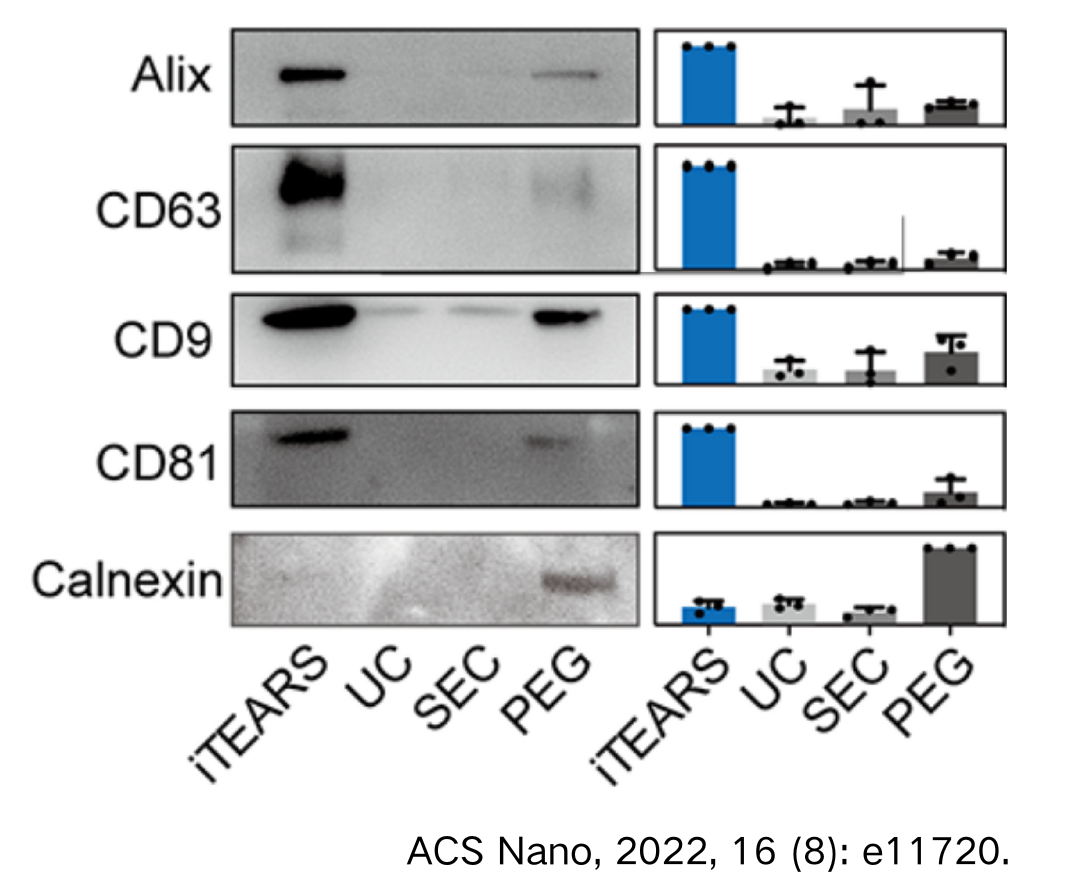
The yield and purity analysis of tear exosome isolated by methods of EXODUS, UC, SEC, and PEG.
A. Total particles of exosomes isolated using EXODUS or PEG from 50 μL of tear (approximately 2 x 1010 particles/mL) showed over a 20-fold and 2-fold increase compared to those isolated from UC and SEC, respectively.
A.
B.
Case 5: Bacterial Culture Medium
(1) Bacterial EV Isolation With EXODUS H-600
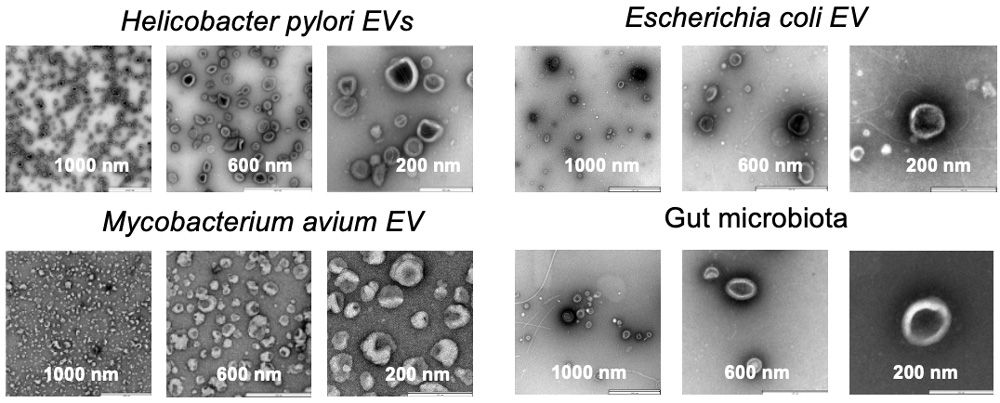
Characterization of bacterial EVs by TEM.
TEM images of EVs derived from Helicobacter pylori, Escherichia coli, Mycobacterium avium, and intestinal microbiota isolated by EXODUS H-600. The EXODUS H-600 is capable of isolating EVs from a variety of bacterial sources, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
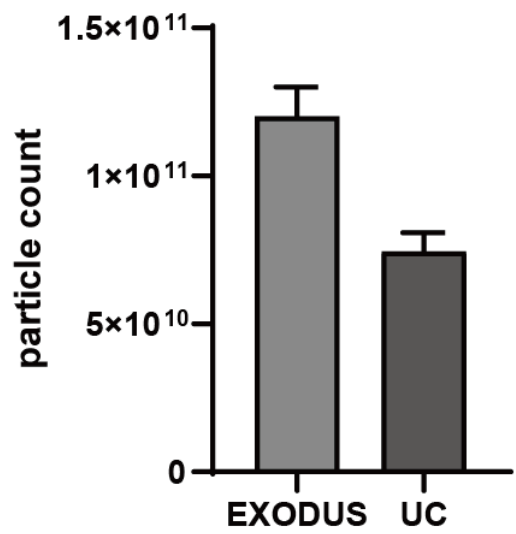
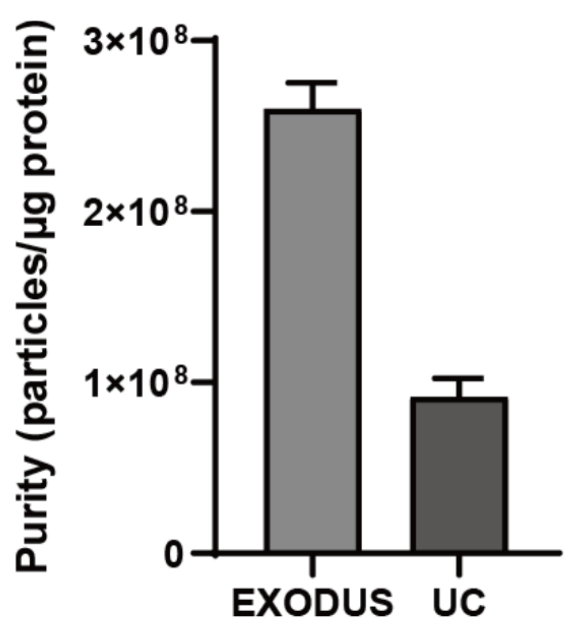
Comparison of yield and purity by using EXODUS H-600 and UC.
EXODUS H-600 achieves higher particle yield and EV purity compared to UC of E.coli EVs.
Case 6: Plant
(1) Plant sample EV isolation with EXODUS T-2800
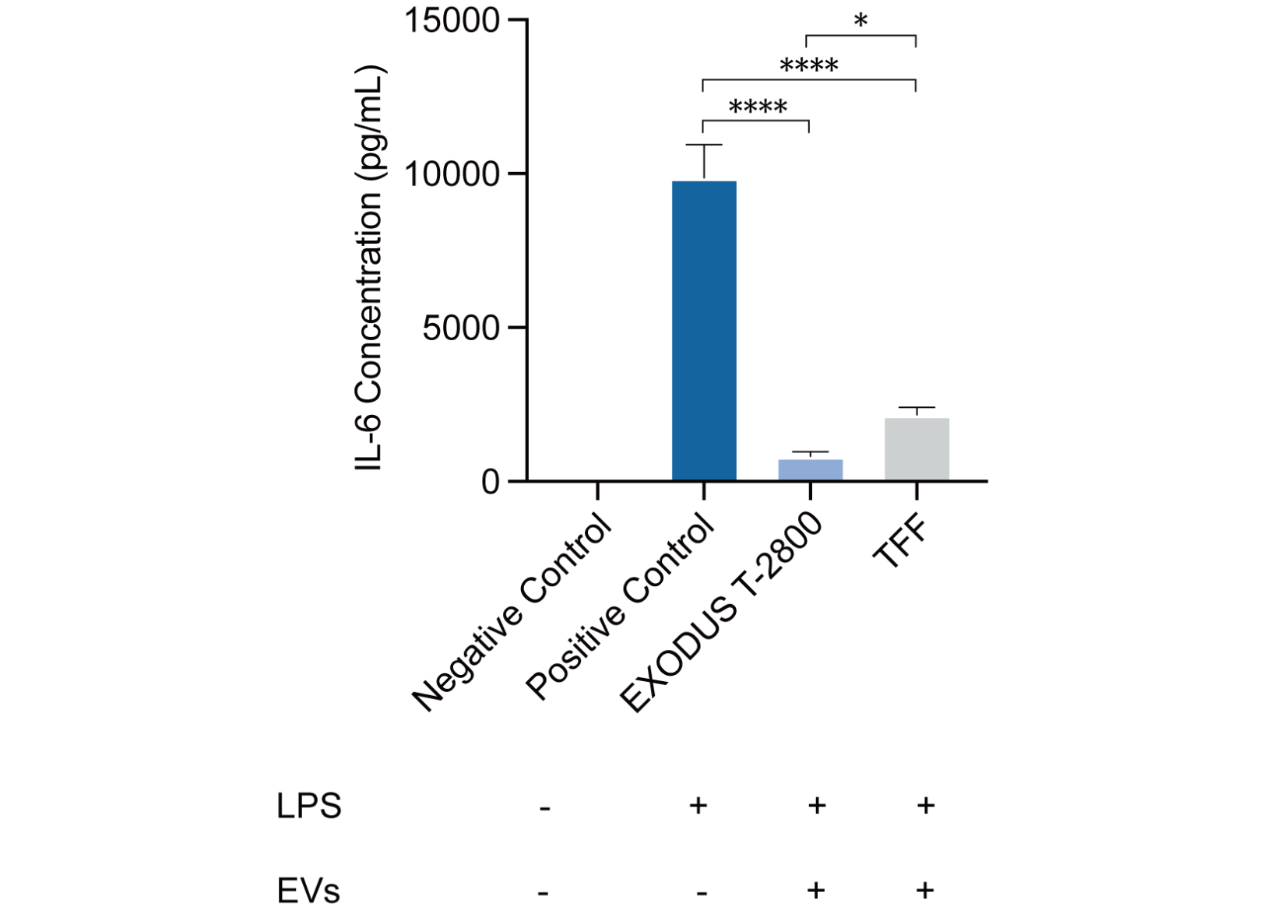
Anti-inflammatory activity results of plant exosomes.
Plant exosomes were purified using EXODUS T-2800 and TFF, and IL-6 anti-inflammatory activity was tested. The purified exosome of EXODUS T-2800 exhibits good anti-inflammatory effects, with efficacy and activity superior to that of the TFF purified exosome.
Inhibition of IL-6 inflammatory factor secretion
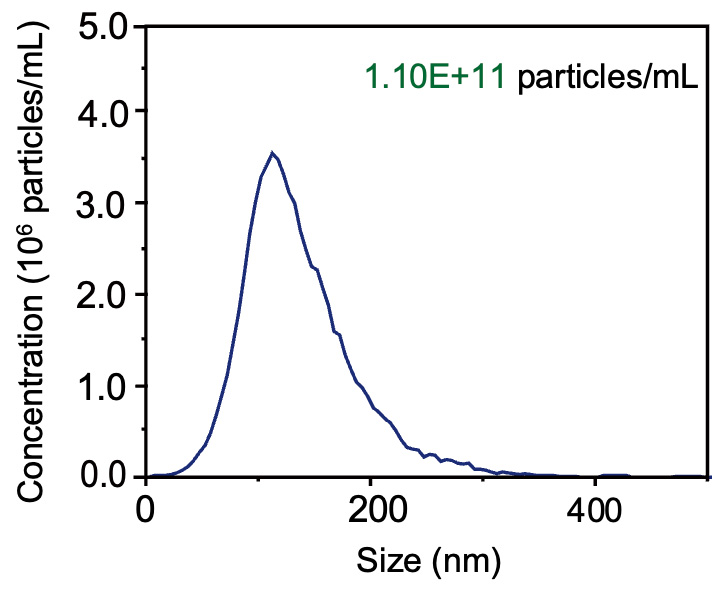
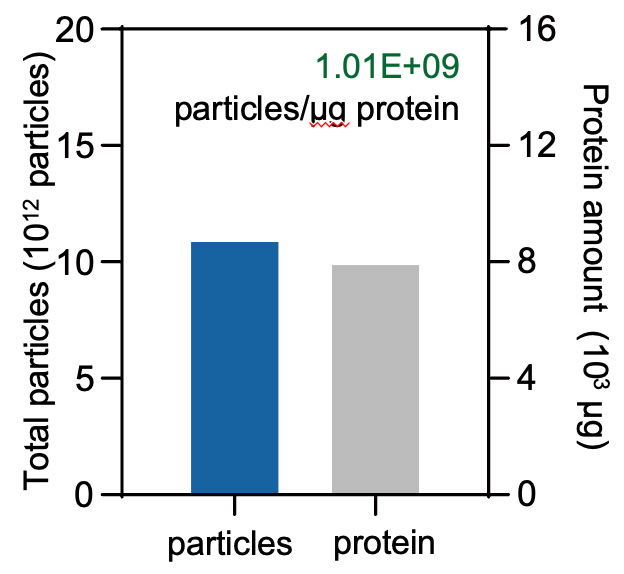
Characterization of plant exosomes isolated by T-2800.
(Left) NTA data shows that the size distribution of the concentration of 1.10×1011 particles/mL. (Right) The particle-to-protein ratio is 1.01×109 particles/μg protein.
Nanoparticle tracking analysis
Particle-to-protein ratio

The Engine, 750 Main Street, Cambridge, MA 02139, United States
Phone: +1 510-377-1762
Email: service@exodusbio.com
© 2025 Exodus Bio. All Rights Reserved.
Built By Metropolis

